Several, but not all, of the human monoclonal antibodies used clinically to prevent patients from becoming severely ill from COVID-19 may not be protective against the omicron variant now sweeping across the United States, researchers reported Jan. 19 in the journal Nature Medicine.
The laboratory study, led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri, tested five antibody combinations including precursor antibodies discovered at Vanderbilt University Medical Center that subsequently were optimized by AstraZeneca and which were authorized for emergency use in patients last month.
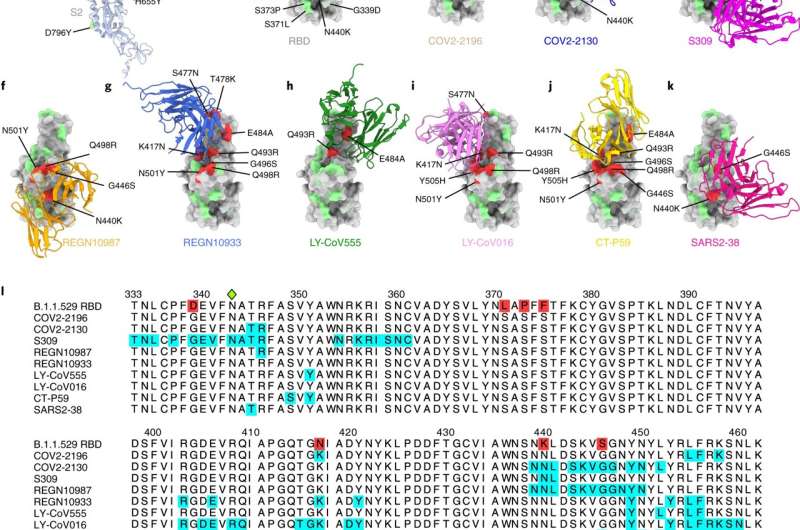
Several antibodies, including those in clinical use by Celltrion, Regeneron and Eli Lilly, completely lost the ability to neutralize the omicron variant in cell culture, whereas the antibodies discovered at VUMC had a reduced neutralizing ability, and an antibody developed by Vir Biotechnology was minimally affected, the study found.
“Omicron escapes recognition by several of the monoclonal antibodies that are being used for therapy,” said James Crowe Jr., MD, director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Center, whose team discovered the monoclonal antibodies later optimized by AstraZeneca into a long-acting antibody combination called Evusheld.
Fortunately, the precursor antibody of Vir Biotechnology’s sotrovimab, “and the prophylaxis antibodies in Evusheld retain substantial though reduced activity,” said Crowe, a coauthor of the paper with VUMC research fellow Seth Zost, Ph.D. “That is good news, since we still have a least one antibody drug we can use for each of the indications, prevention or therapy.”
Most of the monoclonal antibodies used to prevent severe illness from COVID-19 are administered by intravenous infusions. Evusheld currently is the only antibody combination given by intramuscular injection to protect uninfected people from COVID-19.
Evusheld is authorized only for people who are not currently infected with the COVID-19 virus and who are immunocompromised because of medical conditions or treatment for disorders including cancer or who have a history of a severe adverse reaction to a COVID-19 vaccine.
The current study was led by Michael Diamond, MD, Ph.D., a leading expert in viral pathogenesis at Washington University School of Medicine. The loss of neutralizing ability is due to the more than 30 mutations in the omicron “spike” protein, the antibody target, on the surface of the virus.
The loss of inhibitory activity in the study is consistent with the observation that antibody responses generated after vaccination or natural infection also lose substantial inhibitory activity against omicron. That finding may explain in part the rise in symptomatic infections caused by the omicron variant in people who have previously been vaccinated.
The continued identification and use of broadly and potently neutralizing monoclonal antibodies that target the most highly conserved and least likely to mutate portions of the spike protein are needed to protect against omicron and future variants, the researchers concluded.
Source: Read Full Article
