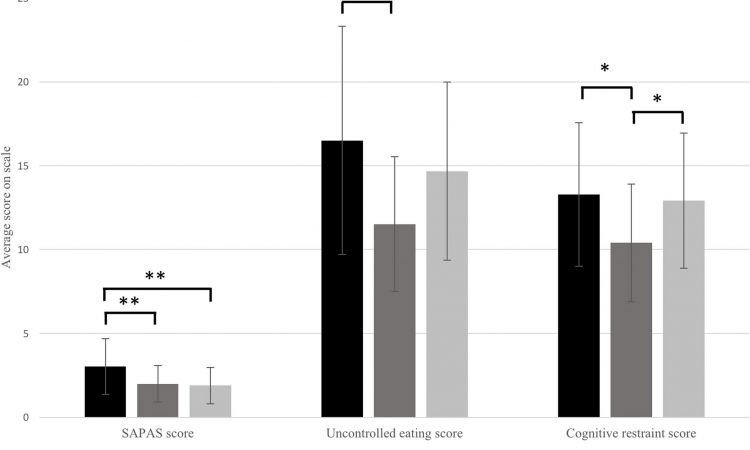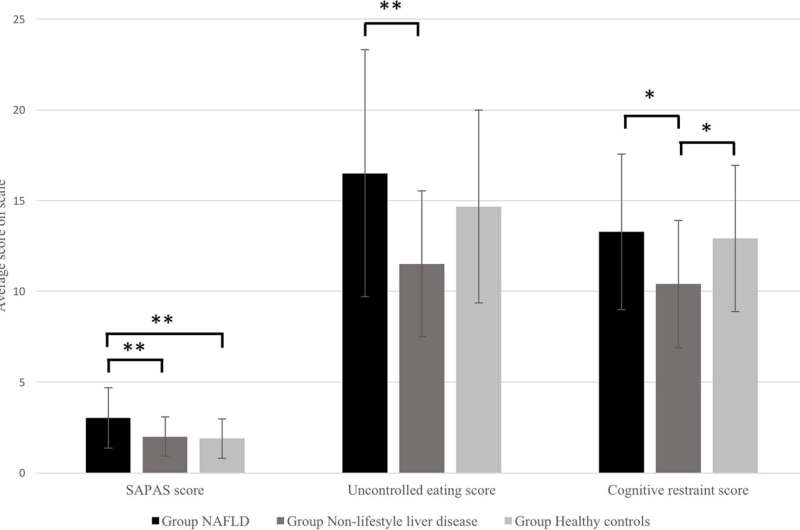
Patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are more likely to suffer with a personality disorder than people without the condition, a new study reveals.
Researchers also discovered that, while NAFLD patients know that they need to watch their diet and exercise to keep the disease in check, they frequently exhibit uncontrolled eating behaviors.
NAFLD has become the most common cause of chronic liver disease in wealthy societies—responsible for a significant rise in liver-related deaths.
Up to one in three people in the UK has fatty liver disease. While in its early stages there may be few symptoms, the disease can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure in at risk individuals such as diabetics.
Non-alcohol steatohepatitis—a more serious form of NAFLD, where the liver has become inflamed—is the most common cause of cirrhosis in industrialized countries where deaths from liver disease have increased fourfold over the last 50 years.
Publishing their findings in BMC Gastroenterology, researchers from the University of Birmingham reveal that NAFLD patients are around three times more likely to have a personality disorder than those people without the disease.
The scientists call for NAFLD patients to be screened for personality disorders—if identified, these mental health disorders should be treated before the patients begin trying to control their diet and exercise more.
Co-author Dr. Jonathan Catling, from the University of Birmingham, commented, “Finding an increased prevalence of personality disorders in NAFLD patients is particularly striking—signifying that it’s not an issue associated with all liver disease, but just those with NAFLD.
“Importantly, it appears not to be a general mental health issue, as neither anxiety nor depression were found to be significantly different between the groups—despite both psychiatric disorders often being associated with chronic liver disease.”
The scientists note that, although simple measures such as changes in diet and increased exercise are proven to prevent disease progression in NAFLD, it is often difficult to persuade patients to follow dietary and exercise programs. This may reflect the fact that such patients are often encouraged to boost their protein and calorie intake to reverse nutritional declines commonly seen in chronic liver disease.
NAFLD patients are aware of the beneficial effects of lifestyle modifications, yet frequently cannot make the necessary changes to an improved lifestyle is poor. Even among patients transplanted for NAFLD two-fifths of patients showed signs of the disease recurring within five years of transplantation.
Dr. Catling added, “Our findings suggest an urgent need to examine attitudes towards diet and exercise so that we can better understand how to motivate NAFLD patients and deliver more effective treatment—preventing disease recurrence after liver transplantation.”
One factor determining a patient’s attitudes towards weight loss is their internal and external ‘locus of control’ (LoC)—or how much control they believe they have over their life events. Patients with a high internal LoC perceive life events to be a result of their own actions and are more likely to be successful in losing weight.
NAFLD sufferers, rather like individuals with substance abuse disorders, may have increased external LoC—seeing life events as out of their control and struggling to make and maintain the necessary changes to their diet and exercise regime that prevent disease progression into the more serious, irreversible stages of the disease.
In 2011, NAFLD was reported as prevalent in up to 25% of the global adult population. The disease is a metabolic disorder characterized by the presence of lipid droplets in the liver with the absence of excessive alcohol consumption.
NAFLD is a global health problem and multi-faceted disease, with the main risk factors being obesity and insulin resistance. Because of the close relationship with obesity, NAFLD’s prevalence continues to be a major public health challenge as western societies battle with rising rates of obesity-related disease.
More information:
E. Asquith et al, Behaviour regulation and the role of mental health in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, BMC Gastroenterology (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s12876-023-02941-x
Journal information:
BMC Gastroenterology
Source: Read Full Article