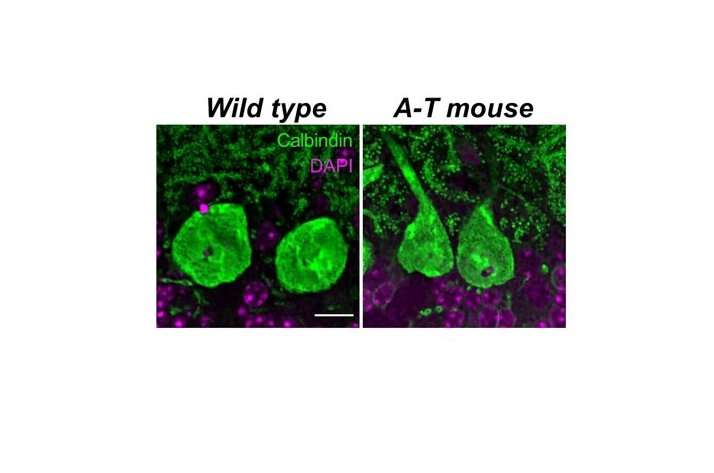
The Lundquist Institute’s investigators have developed a novel mouse model that displays the most comprehensive set of A-T symptoms which provides for the very first time a resource to not only clarify the mechanisms of this neurological dysfunction but also gives researchers a critically needed in vivo model to test future A-T therapeutics. The investigators also demonstrated that Small Molecule Read-Through (SMRT) compounds can restore ATM production. The disease results from a mutation in the A-T mutated gene (ATM). This gene provides instructions for making a protein that helps control the rate at which cells grow and divide. Defects in this gene can lead to abnormal cell death around the body, including the part of the brain that helps coordinate movement. The complete study is published in the journal eLife.
Ataxia Telagiectasa (A-T) is a rare childhood disease. Ataxia refers to uncoordinated movements, such as walking. The telagiectasias are enlarged blood vessels found just below the skin. It is an inherited disease passed down from parents to children and is an autosomal recessive genetic trait. An autosomal recessive disorder means two copies of an abnormal gene must be present in order for the disease or trait to develop, that is, both parents must provide a copy of a nonworking gene for the child to have symptoms of the disorder. Boys and girls are equally affected.
Source: Read Full Article
