Israel has had a successful vaccination campaign against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), as over 80% of its adult population has been fully vaccinated with two doses of the Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine as of July 28, 2021.
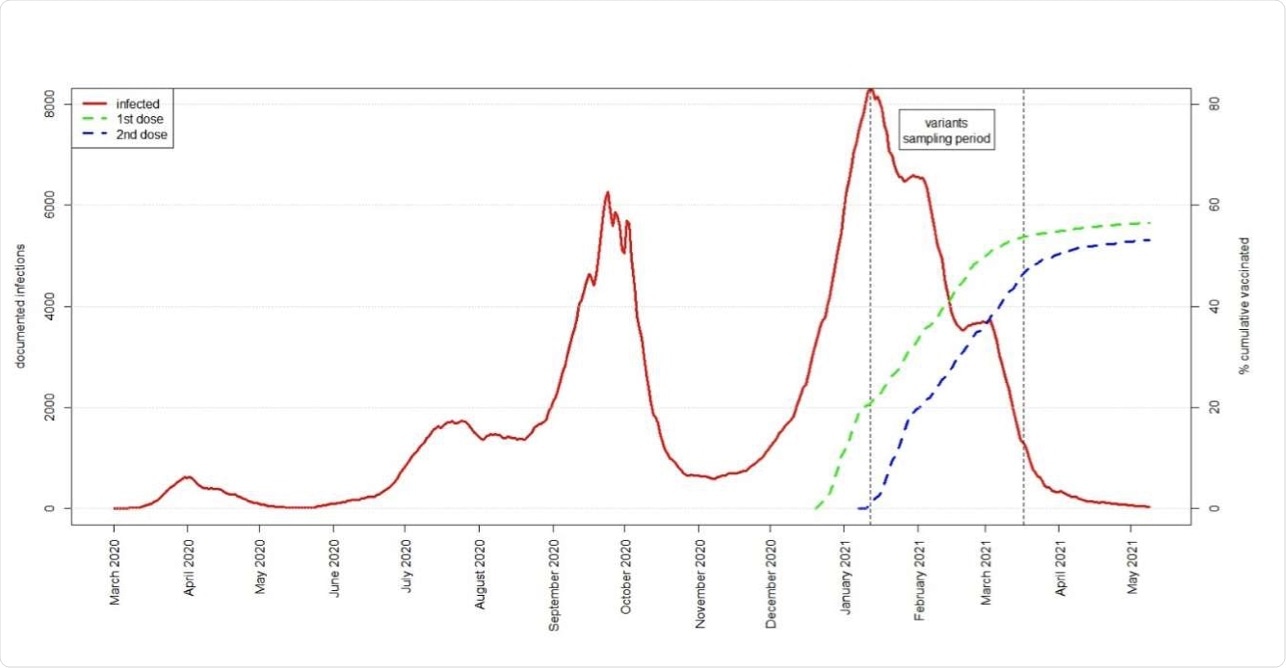
This excellent vaccination rate has helped curtail the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak to a significant extent. As of June 1, 2021, the country lifted all COVID-19-related emergency restrictions except the mask requirement in indoor environments and international travel restrictions.
 Study: BNT162b2 Vaccination efficacy is marginally affected by the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 variant in fully vaccinated individuals.
Study: BNT162b2 Vaccination efficacy is marginally affected by the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 variant in fully vaccinated individuals.
Evaluating vaccine protection against B.1.351
One major concern with SARS-CoV-2 is its ability to mutate and give rise to new variants that potentially possess partial or full immune escape capabilities. Researchers from Israel recently evaluated the efficacy of the Pfizer vaccine against the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 (Beta) variant in a study that is currently available in the preprint server medRxiv*.
In their work, selected polymerase chain reaction (PCR) positive samples of interest were sequenced by the Central Virology Laboratory of The Ministry of Health. The researchers used logistic regression with vaccination status as the key explanatory variable and the variant type as the dependent variable.
The researchers also controlled for sex, age, subpopulation, place of residence, and time of the sample. The odds ratio for a vaccinated patient to have the B.1.351 as compared to the B.1.1.7 (Alpha) variant was estimated among vaccinated and unvaccinated subjects who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2.
Study results
The study showed the presence of 19 cases (3.2%) of the B.1.351 variant in participants who were vaccinated for more than 14 days before the positive sample and 88 cases (3.5%) among the unvaccinated participants. The odds ratio was estimated to be 1.29. This shows that the estimated efficacy of the Pfizer vaccine against the B.1.351 variant was 94%, assuming the efficacy of this vaccine against the B.1.1.7 variant to be 95%.
“Our results suggest that from 14 days following the second vaccine dose, the efficacy of BNT162b2 vaccine is at most marginally affected by the B.1.351 variant.”
Despite immune escape concerns caused by the B.1.351 variant, the Pfizer BNT162b2 vaccine appears to offer substantial immunity against both the B.1.351 and the B.1.1.7 variants. The results suggest that 14 days after the second dose of the vaccine, the efficacy of the vaccine is only slightly affected by the B.1.351 variant.
Analyzing positive cases between 1-13 days of the second dose
This study included a larger number of vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals as compared to a previous study conducted in Israel. Also, the main analysis of this work focused on vaccinated patients who were infected with the B.1.351 or the B.1.1.7 variant more than 2 weeks after their second vaccination dose.
Overall, the researchers did not find a statistically significant decrease in protection by the Pfizer vaccine. However, a sub-analysis examined vaccinated cases occurring between 1-13 days after the second dose and found an increase in the proportion of the B.1.351 variant compared to that in unvaccinated cases, with an estimated odds ratio of 2.62.
According to the authors, there was no overlap of data between the two studies despite both being conducted in Israel. On integrating the findings from both studies, the authors support the hypothesis that a higher immunity level is required for protection against the B.1.351 variant. This suggests different efficacy levels of the Pfizer vaccine against the B.1.351 and B.1.1.7 variants during the first 2 weeks after patients receive their second dose of the vaccine.
The authors mentioned that the next generation of COVID-19 vaccines will need to be modified to combat different variants of concern (VoCs). However, the currently available vaccines may still offer substantial immunity against both current and future variants of concern.
“The fact that the B.1.351 variant, which was first diagnosed in Israel January 2021, concomitantly with the start of the vaccination program, has not caused significant community transmission in Israel is further encouraging evidence supporting the ability of two doses of the BNT162b2 vaccine combined with high coverage to halt transmission.”
*Important notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific reports that are not peer-reviewed and, therefore, should not be regarded as conclusive, guide clinical practice/health-related behavior, or treated as established information.
- Mor, O., Zuckerman, N. S., Hazan, I., et al. (2021). BNT162b2 Vaccination efficacy is marginally affected by the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 variant in fully vaccinated individuals. medRxiv. doi:10.1101/2021.07.20.21260833. https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.07.20.21260833v1
Posted in: Medical Research News | Disease/Infection News | Pharmaceutical News
Tags: Coronavirus, Coronavirus Disease COVID-19, Efficacy, immunity, Laboratory, Next Generation, Polymerase, Polymerase Chain Reaction, Respiratory, SARS, SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Syndrome, Vaccine, Virology

Written by
Susha Cheriyedath
Susha has a Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.) degree in Chemistry and Master of Science (M.Sc) degree in Biochemistry from the University of Calicut, India. She always had a keen interest in medical and health science. As part of her masters degree, she specialized in Biochemistry, with an emphasis on Microbiology, Physiology, Biotechnology, and Nutrition. In her spare time, she loves to cook up a storm in the kitchen with her super-messy baking experiments.
Source: Read Full Article
