Body Mass Index (BMI) is a measurement of a person’s weight with respect to his or her height. It is more of an indicator than a direct measurement of a person’s total body fat.
BMI, more often than not, correlates with total body fat. This means that as the BMI score increases, so does a person’s total body fat.
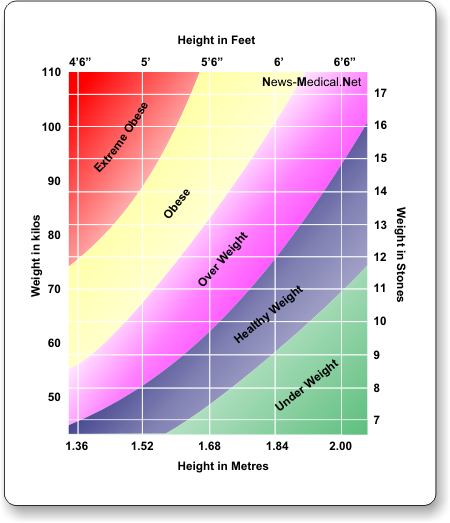
The WHO defines an adult who has a BMI between 25 and 29.9 as overweight – an adult who has a BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese – a BMI below 18.5 is considered underweight, and between 18.5 to 24.9 a healthy weight .
BMI calculation
BMI in an individual is calculated by the use of a mathematical formula. It can also be estimated using tables in which one can match height in inches to weight in pounds to estimate BMI. There are convenient calculators available on internet sites that help calculate BMI as well.
The formula is – BMI = (Weight in kilograms) divided by (Height in metres squared)
A normal BMI score is one that falls between 18.5 and 24.9. This indicates that a person is within the normal weight range for his or her height. A BMI chart is used to categorize a person as underweight, normal, overweight, or obese.
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | Weight Status |
| Below 18.5 | Underweight |
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal |
| 25.0 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30.0 plus | Obese |
Clinical relevance of BMI
BMI is an indicator of total body fat in many individuals. Thus it is considered as an indicator of health risk.
BMI is used by healthcare professionals to screen for overweight and obese individuals. The BMI is used to assess a person’s health risks associated with obesity and overweight.
For example those with a high BMI are at risk of:-
- high blood cholesterol or other lipid disorders
- type 2 diabetes
- heart disease
- stroke
- high blood pressure
- certain cancers
- gallbladder disease
- sleep apnea and snoring
- premature death
- osteoarthritis and joint disease
BMI, however, is one of the tools that are used to calculate healthy risk. Other factors such as blood pressure, cholesterol level, blood sugar level, family history of heart disease, age, gender, waist circumference, level of physical activity, menopause status, smoking status etc. are also taken into consideration while assessing health risk.
Is BMI applicable for all?
For most people, BMI can be used to provide a good measure of obesity. But BMI fails to provide actual information on body composition like amount of muscle, bone, fat, and other tissues.
In some persons BMI is a more accurate measure of body fat than others. For example, persons who are very muscular may fall into the “overweight” category when they are actually healthy and very fit. These persons with a very low body fat percentage could have the same BMI score as someone who is overweight.
Similarly, an elderly and frail individual person may be in the normal weight category when they have little muscle mass and a high percentage of body fat.
BMI, when used for children and adolescents who are still growing, those with large body frames or petite builds, pregnant women and highly muscled individuals thus need to be assessed and interpreted carefully.
Sources
- http://departments.mercer.edu/payroll/BMI.pdf
- http://www.cnpp.usda.gov/publications/nutritioninsights/insight16.pdf
- http://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/obesity/bmi/pdf/BMI_execsumm.pdf
- http://www.nhs.uk/Tools/Pages/Healthyweightcalculator.aspx
Further Reading
- All Obesity Content
- What is Obesity?
- Causes of Obesity and Overweight
- Obesity, What Can be Done?
- Obesity and Fast Food
Last Updated: Feb 27, 2019

Written by
Dr. Ananya Mandal
Dr. Ananya Mandal is a doctor by profession, lecturer by vocation and a medical writer by passion. She specialized in Clinical Pharmacology after her bachelor's (MBBS). For her, health communication is not just writing complicated reviews for professionals but making medical knowledge understandable and available to the general public as well.
Source: Read Full Article
